Introduction To Pointers
The
most excruciating pain is delivered when we finally work with POINTERS. Learning POINTER brings us closer to
the point where Dennis Ritchie directly/indirectly gave rise to OOP referencing
method knowingly/unknowingly.
Let’s understand the trickiest and the most important
concept of C Programming. à
à
Pointers
ß
Definition:-- Pointer
is a special data type which is
derived from basic data
Types.
·
It is called a derived data type.
·
It takes the values from 0 to 65535 on 64K RAM.
·
It’s associated with the following three
concepts as shown below.
·
Pointer stores memory address of other
variables i:e a reference
1. Pointer Constants
·
The memory addresses are known as Pointer
Constants.
·
These cannot be changed but can only be used to
store data values.
2. Pointer Values
·
Memory addresses assigned to variables by the
system are called Pointer Values.
3.
Pointers Variables
·
A variable that holds address of another variable is
known as Pointer Variable.
In
order to understand the above 3 important concepts related to pointers. Let’s
see the syntax and how to use pointers.
à Syntax ß
Declaration and Definition:
Note: The
position of * between type and identifier is immaterial.
Eg:- int *p
Int * p
int * p
All the declarations are just alike…
à Accessing Variables through Pointers ß
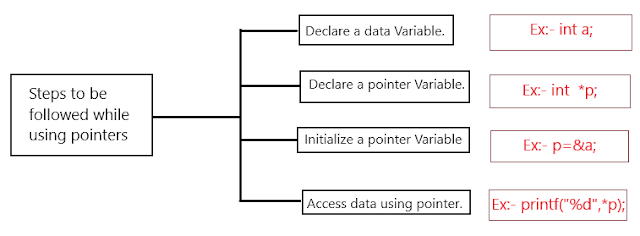
These are the steps to be followed to access a
variable through Pointers.
Logical
Representation in Memory will be :à
à Advantages and Disadvantages ß
Advantages: -
·
Pointers
provide direct access to memory
·
Pointers
provide a way to return more than one value to the functions
·
Reduces the
storage space and complexity of the program
·
Reduces the
execution time of the program
Disadvantages:
·
Uninitialized
pointers might cause segmentation fault.
·
Dynamically
allocated block needs to be freed explicitly. When not freed causes memory
leak.
·
Pointers are
slower than normal variables.
·
Hard to
debug.
Uses:
·
Pointers
allows us to perform dynamic memory allocation and deallocation.
·
Pointers
helps us to build complex data structures like linked list, stack, queues,
trees, graphs etc.
·
Helps
in Call By Reference method of calling in C.
Will be posting more ……….
Keep Smiling and don't forget to contact me for further assistance.
Your Friendly Coder.
SPrince




Comments
Post a Comment
Add related suggestions and Leave comments if you want your posts to get shared